Prof. Hong Tang has devised a process of nanofabrication to create a silicon chip that contains all the components needed for a quantum information processor. Their results are published today in Nature Communications.
The potential benefits of quantum technology are huge. Theoretically, it can complete in seconds certain tasks - like simulations of complex chemical processes or searching through huge amounts of data - that would require years for current technology.
Putting it into execution, though, is not so easy. For one, quantum systems, like single atoms or single photons, are extremely delicate and can be thrown off by various environmental influences – electrical, magnetic, and thermal among them. So it’s important that the system be protected from the environment. At the same time, though, it needs to be controlled. That can be done now on a very small scale, but a number of factors - expense and the amount of technology required, for instance - make it very difficult to control many quantum systems at once.
In a step toward solving this, the lab of Prof. Hong Tang has devised a process of nanofabrication to create a silicon chip that contains all the components needed for a quantum information processor. Their results are published today in Nature Communications.
“We can make a lot of these nanodevices easily by copying our design hundreds or thousands of times, without much additional effort or cost,” said Carsten Schuck, post-doctoral researcher and lead author of the paper. “It’s similar to what people in the semiconductor industry do, who developed the technology to make billions of transistors.”
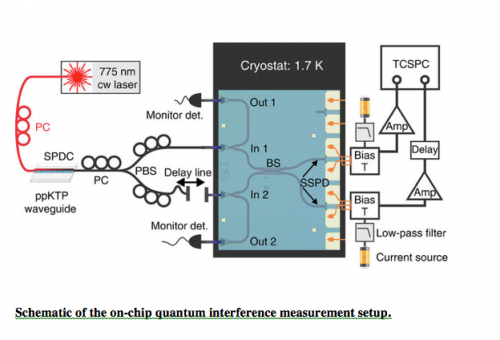
The two essential requirements for a scalable quantum information processor are quantum interference (in which a photon – able to be in more than one place at a time – crosses its own path) and single-photon detectors. The chip that the researchers designed contains a nanophotonic waveguide, which can guide light into small spaces and to wherever is needed on the chip. It also has a directional coupler that can split a light beam into two identical beams, or conversely, combine two beams into one output. Schuck compares his system to state-of-the-art experimental setups consisting of hundreds of bulky optical components to control a quantum system.
“Where we use a tiny silicon chip you used to need a whole room full of equipment to control a quantum system,” he said. “If you wanted to manipulate another quantum system, you needed another room and the money to buy all the equipment again. But if I want to manipulate another photon, I put an additional circuit on the same square-centimeter silicon chip, which takes a couple extra seconds during nanofabrication.”
With this research, Schuck said the research team should eventually realize a programmable optical quantum processor that can run a quantum algorithm. The scalability of the nanofabrication routines for silicon chips will then allow them to solve problems difficult for classical computers. He added that the same technology could also be useful for other applications, such as building extremely sensitive sensors or secure communication devices.
http://seas.yale.edu/news-events/news/quantum-technology-chip